Here’s a full 5-day healthy lightweight backpacking meal plan.
You’ll notice that each day of this meal plan is about 55% fat, 20% protein, and 25% carbohydrate. It’s based around whole foods, it’s anti-inflammatory and it’s suitable for stoveless meal prep (optional).
This healthy high fat approach helps me reduce pack weight, eliminate bonking, reduce hiker hunger, and decrease digestive issues. If you’re curious about the science and rationale of how I landed on this approach after years of experimentation, check out this post.
You’ll notice that this diet is a bit different than the standard, processed thru-hiker diet. It’s not perfect, but in general, this meal plan is designed to:
- be low in inflammatory ingredients
- be largely unprocessed & emphasize food quality (Because your food choices should be about more than just calories and here’s why)
- be organic/free-range/grass-fed when possible (so I can avoid the damage of glyphosate on both my body and the environment)
- emphasize nutrient density
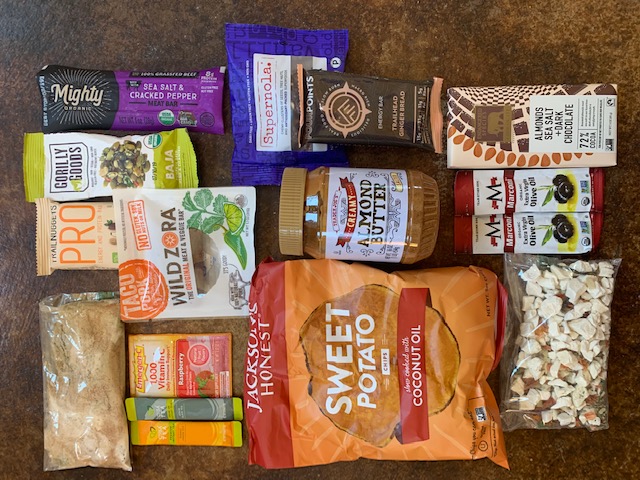
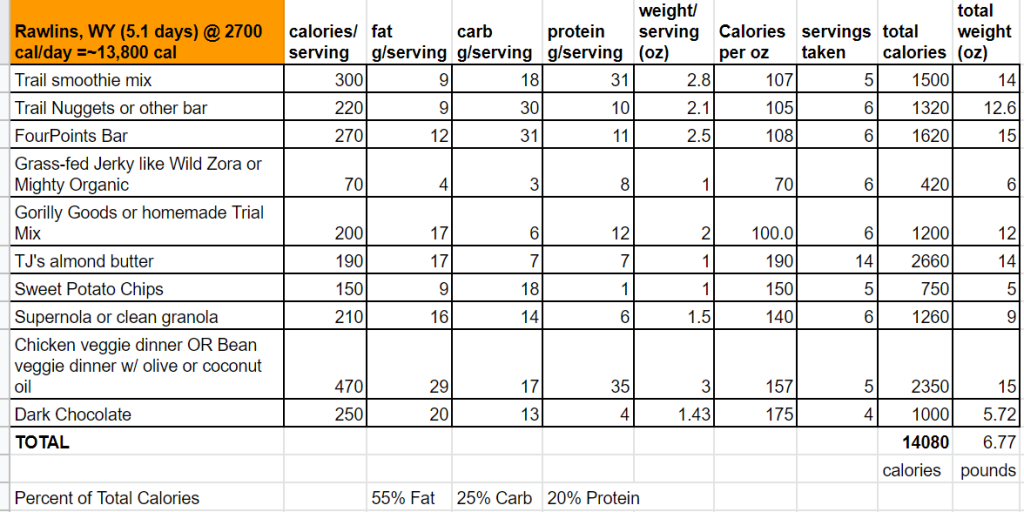
The following meal plan was pulled straight from my spreadsheet for my Continental Divide Trail resupply plan. As such, it’s based on my calorie needs and food preferences. Dial in how much food is right for you and get a step by step guide to meal planning in this course.
The 5 days shown here is a box I’m sending around mile 1200, so it’s based on ~2700 calories per day. The total weight for this 5 days of food is 6.77 pounds or about 1.35 pounds of food per day. This is significantly lower than the commonly recommended 2 pounds per day.
I hope this gives you some ideas for your own backpacking meal if you’re looking for something a bit less junk food-y. It’s somewhat repetitive, but I appreciate the simplicity of that. It makes shopping in bulk easier and I can add variety by rotating through different varieties/flavors. For example, with a trail mix, it might be almonds, coconut flakes, dried cranberries, and ginger powder in one box, then walnut, cacao nibs, banana chips, and cinnamon in the next box.
The chart represents all the food for 5 days and the photos show what each day would look like. Post your Q’s or comments below.